GI Bleeding Risk: What You Need to Know About Medications and Stomach Damage
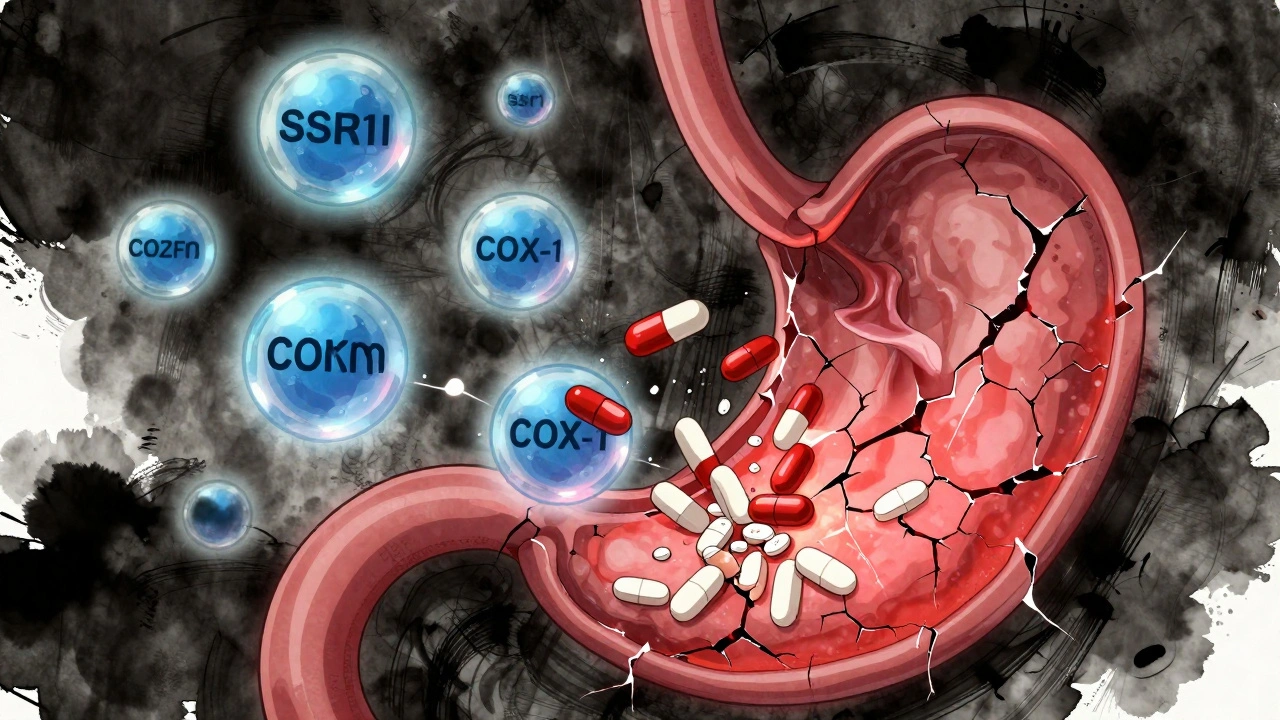
When you take a pain reliever or blood thinner, you might not think about your stomach—but GI bleeding risk, the chance that medications cause dangerous internal bleeding in the digestive tract. Also known as gastrointestinal bleeding, it’s not rare, and it doesn’t always come with warning signs until it’s serious. This isn’t just about ulcers. It’s about how everyday drugs quietly wear down your stomach lining, especially if you’re over 60, taking multiple meds, or have a history of stomach issues.
NSAID safety, how nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen affect your gut is a big part of this. These drugs block protective enzymes in your stomach, leaving it exposed to acid. The longer you take them, the higher your risk. And it’s not just NSAIDs. Blood thinners like warfarin, a common anticoagulant used to prevent clots, can turn a small tear into a life-threatening bleed. Even aspirin, often thought of as harmless, adds to the risk when taken daily. These drugs don’t need to cause pain to be damaging—you can have internal bleeding without feeling a thing until you’re dizzy, weak, or passing dark, tarry stools.
Who’s most at risk? Older adults, people on multiple medications, those with a history of ulcers or H. pylori infection, and anyone taking steroids or SSRIs alongside NSAIDs. It’s not just about the drug—it’s about the combo. A simple painkiller might be fine alone, but with blood pressure meds, antidepressants, or even fiber supplements that slow digestion, the risk climbs. Monitoring isn’t just for doctors. If you’re on long-term meds, pay attention to unexplained fatigue, black stools, or sudden stomach pain. These aren’t normal side effects—they’re red flags.
What you’ll find below are real, practical posts that break down exactly how these risks show up, who’s most vulnerable, and what you can do to protect yourself. From how GI bleeding risk ties into generic drug switching, to why some people react worse to certain pills because of inactive ingredients, to how to spot early signs before it’s an emergency—these aren’t theoretical discussions. They’re based on patient experiences, clinical data, and what actually works in everyday life. You won’t find fluff here. Just clear, no-nonsense info to help you stay safe while taking the meds you need.